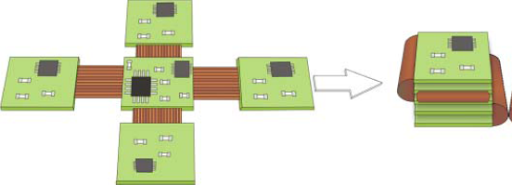
Flex Rigid PCB PI Stiffener electromagnetic shielding film| YMS PCB
Applications:
As the name implies, rigid-flex printed circuit boards(PCBs) are the composite boards of rigid boards and flexible boards. Most rigid-flex circuits are multi-layered. A rigid-flex PCB can include one/several flex boards and rigid boards, which are connected through internally/externally plated-through holes.
Rigid Flexible PCB: Bend radius controls the flexibility of the flex portion of the board. The thinner the material the lower the bend radius and the more flexible the flex section.
Rigid flexible PCBs offer a wide range of applications, from military weapons and aerospace systems to mobile phones and digital cameras. Rigid flexible plate manufacturing is increasingly used in medical devices, such as pacemakers, to gain space and the ability to reduce weight. The use of rigid flexible PCBS also has advantages that can be used in military weapons and weapon control systems in consumer products.
Parameters
Layers: 4L Rigid flex PCBs with PI Stiffener
Board Thinkness:0.8mm+/-0.1mm
PCB thickness in flex section:0.1mm+/-0.03mm
Base Material:PI+FR4
Min mechanical Holes:0.2mm
Minimum Line Width/Clearance:0.1mm/0.1mm(4mil/4mil)
Minimum Clearance between Inner Layer PTH and Line: 0.2mm
Size:150mm×20mm
Aspect Ratio:4 : 1
Surface treatment:OSP
Speciality: Rigid flex pcb core+core stackup,PI Stiffener,With the structure of electromagnetic shielding film
Differential impedance 100+7/-8Ω
Applications: Consumer electronics
Flexibility:
Rigid flexibility not only maximizes space and weight but also greatly improves reliability, eliminating the need for many welded joints and weak wires that can easily create connection problems. These are just a few examples, but rigid flexible PCBS can be used in almost all advanced electrical applications, including test equipment, tools, and automobiles. Besides the benefits mentioned above, other common advantages of rigid-flex PCBs include high circuit density, excellent thermal dissipation and chemical resistance, etc. All in all, rigid-flex PCBs combine all the benefits of hard PCB and flexible PCB while complementing the disadvantages.
This kind of PCB is an optimal solution to design reliable and robust circuits for smart wearable devices and other industries. YMS has a strict quality control system to ensure the rigid-flex boards manufactured and assembled correctly with high-quality standards.
If you need more details like quotation or order, contact us kell@ymspcb.com now.
Rigid-flex PCBs introduction:
As the name implies, rigid-flex printed circuit boards(PCBs) are the composite boards of rigid boards and flexible boards. Most rigid-flex circuits are multi-layered. A rigid-flex PCB can include one/several flex boards and rigid boards, which are connected through internally/externally plated-through holes.
YMS Rigid Flex PCB manufacturing capabilities:
| YMS Rigid Flex PCB manufacturing capabilities overview | ||
| Feature | capabilities | |
| Layer Count | 2-20L | |
| Rigid-Flex Thickness | 0.3mm-5.0mm | |
| PCB thickness in flex section | 0.08-0.8mm | |
| copper Thickness | 1/4OZ-10OZ | |
| Minimum line Width and Space | 0.05mm/0.05mm(2mil/2mil) | |
| Stiffeners | Stainless steel,PI, FR4 ,Aluminum etc. | |
| Material | Polyimide Flex+FR4,RA copper, HTE copper, polyimide, adhesive,Bondply | |
| Min mechanical Drilled Size | 0.15mm(6mil) | |
| Min laser Holes Size: | 0.075mm(3mil) | |
| Surface Finish | Suitable Microwave/RF PCB urface finishes: Electroless Nickel, Immersion Gold, ENEPIG, Lead free HASL,Immersion Silver.etc. | |
| Solder Mask | Green, Red, Yellow, Blue, White, Black, Purple, Matte Black, Matte green.etc. | |
| Covrelay (Flex Part) | Yellow Coverlay, WhiteCoverlay,Black Coverlay | |
| Common-Used FPC Stiffener Thickness | ||
| Stiffener Material | Usual Thickness | Unusual Thickness |
| FR-4 | 0.2mm(8mil) | 0.1mm(4mil) |
| 0.3mm(12mil) | 0.9mm(35mil) | |
| 0.4mm(16mil) | 1.1mm(43mil) | |
| 0.5mm(20mil) | 1.3mm(51mil) | |
| 0.6mm(24mil) | 1.4mm(55mil) | |
| 0.7mm(28mil) | 1.6mm(63mil) | |
| 0.8mm(32mil) | ||
| 1.0mm(39mil) | ||
| 1.2mm(47mil) | ||
| 1.5mm(59mil) | ||
| Polyimide (PI) | 0.1mm(4mil), | 0.075mm(3mil) |
| 0.15mm(6mil), | 0.125mm(5mil) | |
| 0.2mm(8mil), | 0.175mm(7mil) | |
| 0.25mm(10mil) | 0.225mm(9mil) | |
| 0.275mm(11mil) | ||
| Stainless Steel | 0.1mm(4mil) | 0.45mm(18mil) |
| 0.15mm(6mil) | ||
| 0.2mm(8mil) | ||
| 0.25mm(10mil) | ||
| 0.3mm(12mil) | ||
| 0.35mm(mil) | ||
| 0.4mm(16mil) | ||
| 0.5mm(20mil) | ||
| 1.5mm(59mil) | ||
Metal clad pcb
Aluminum core pcb
High Tg material PCB
Read more news
1. What is copper plating in PCB
2. What is copper thickness in PCB
Flex Rigid PCB PI Stiffener electromagnetic shielding film| YMS PCB Related Video: